Hide My WP Honest Review 2026
What Does Hiding a WordPress Site Mean?
Sometimes hiding a WordPress website can be a good idea if you want to protect it and keep it private. Essentially, it is about preventing the search engines from listing your website and hiding details like WordPress version, as well as restricting access to your pages.
Reducing the Risk of Attacks
It is beneficial as hackers are usually using public websites to identify weak plugins or outdated themes. If you are less visible, you become less attractive for the attackers.
If you are creating a new website, changing the design, or doing a client project, hiding your work will keep your unfinished content secret. Also, it will prevent search engines from indexing your half-ready pages, which is detrimental to SEO.
For membership sites, internal company sites, or subscription platforms, keeping the content login-protected ensures the confidentiality of the information.
Site hiding should not be considered as a security tool at all. It does not eliminate the need for regular updates, setting strong passwords, backups, and using trusted plugins. In that case, hiding can be considered as a further safety measure. It helps to lower the number of unwanted visitors and gives you a chance to fix the problems before the whole world sees your site.
Reason to use this plugin
This approach focuses on hiding and hardening WordPress URLs and endpoints without modifying core files or folders. All files remain in their default locations; only access paths and exposure are controlled. This ensures maximum compatibility with themes and plugins.
1. WordPress Permalink Customization
- Default WordPress permalinks are modified to prevent common URL-based attacks.
- Internal files and folders remain unchanged; only access routes are controlled.
2. Login Page Protection (wp-login.php)
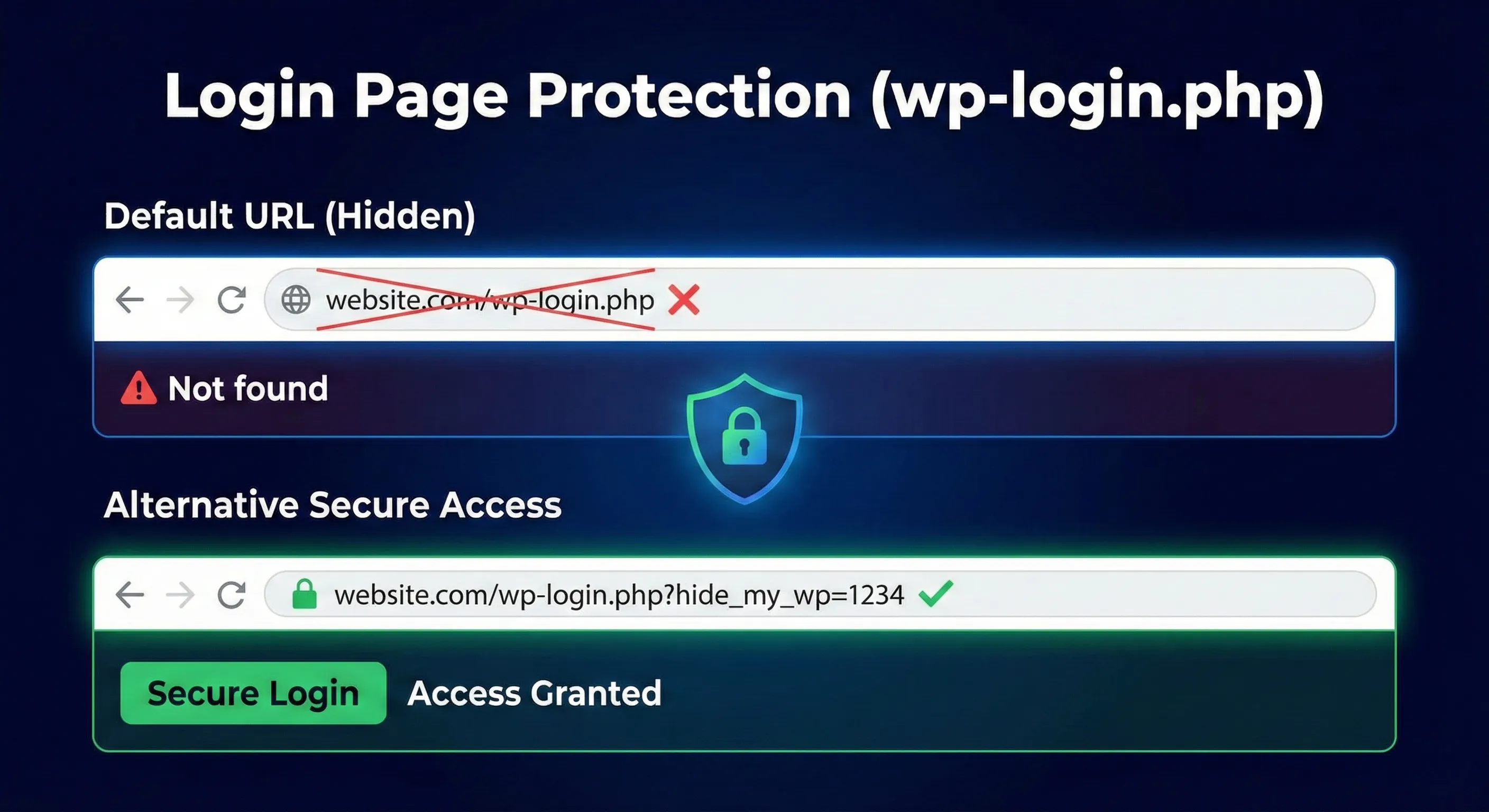
Default URL (Hidden):
/wp-login.php→ Not found
Alternative Secure Access:
/wp-login.php?hide_my_wp=1234
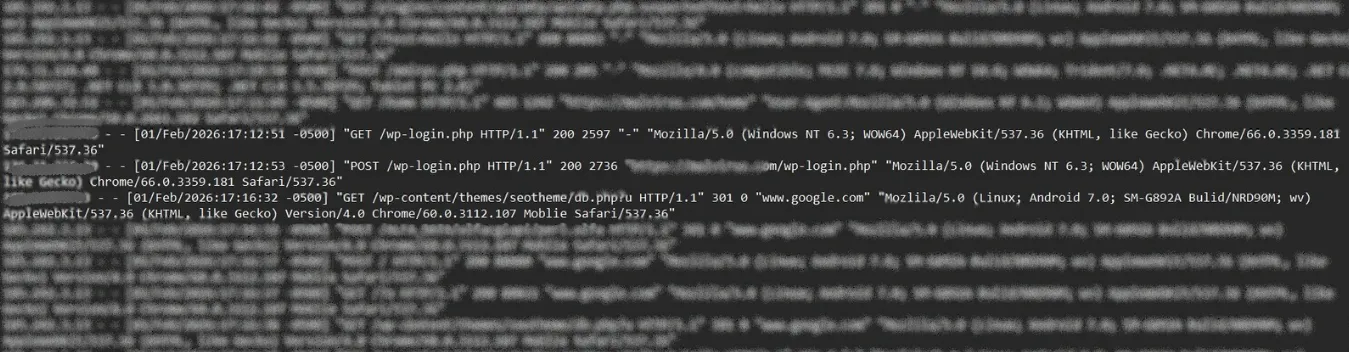
The image shows server access logs indicating a WordPress brute-force login attack. Repeated GET and POST requests target /wp-login.php from multiple devices and user agents. This automated pattern suggests credential guessing attempts and highlights the need for strong passwords, login limits, and additional security measures.
3. Admin Panel Protection (wp-admin)
/wp-admin/→ Not found
Optional Custom Admin Path:
/my-admin/
4. Theme Directory Obfuscation
- Theme directory paths are renamed.
- Theme metadata is removed from stylesheets.
- Default WordPress CSS classes are replaced.
- CSS files are minified.
Example:
- New:
/template/main.css - Old:
/wp-content/themes/twentytwelve/style.css
5. Plugin Directory Protection
- Plugin directory paths are changed.
- Plugin names are hashed.
- Direct PHP file access is denied.
Examples:
/modules/95578af5/shortcodes.css/modules/95578af5/shortcodes.php→ Access denied
6. Core Directory & URL Masking
| Component | New URL | Old URL |
|---|---|---|
| Uploads | /file/test-image-landscape.jpg | /wp-content/uploads/ |
| Includes | /lib/js/jquery/jquery.js | /wp-includes/js/jquery/jquery.js |
| AJAX | /ajax.php (Output: 0) | /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php |
7. WordPress Query URL Replacement
New Query URLs (Working):
/?article_id=1/?user=1/?find=hide
Old Default Queries (Disabled):
/?p=1– Nothing happens/?author=1– Nothing happens/?s=hide– Nothing happens
8. Author URL Customization
New Options:
/admin/profile/admin(optional)
Disabled:
/author/admin→ Not found
9. Feed URL Control

New Feed URLs:
/index.xml/cat/aciform/index.xml
Disabled Default Feeds:
/feed/→ Not found/cat/uncategorized/feed/→ Not found
10. Hiding Default WordPress Files
/readme.html→ Not found/license.txt→ Not found
11. Archive & Taxonomy Restrictions
- Date archives (
/2012/09/) → Not found - Monthly archives (
/?m=201209) → Nothing happens - Categories, tags, pages, and posts can be disabled if not required.
12. Additional Security & Optimization Features
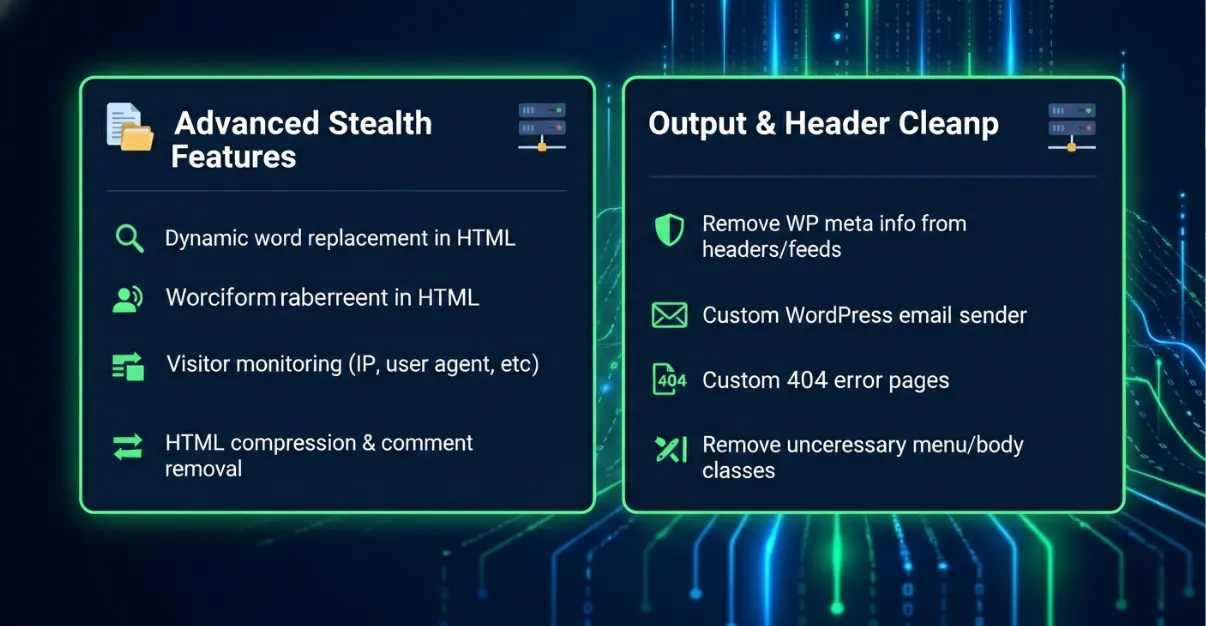
- Dynamic replacement of any word in HTML output
- Visitor monitoring with IP, user agent, referrer, and username
- HTML compression and source code comment removal
- Removal of WordPress meta information from headers and feeds
- Custom WordPress email sender
- Custom 404 error pages
- Removal of unnecessary menu classes
- Cleanup of body classes
13. Built-in Security Protection
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) protection
- SQL Injection protection
- Command Injection protection using built-in IDS
This method significantly reduces WordPress fingerprinting while maintaining full compatibility, performance, and security. It emphasizes obfuscation, access control, and cleanup without modifying core WordPress files, making it a safe and effective hardening approach.


