What are SSL and TLS? Types, Uses and Automation
Understanding SSL/TLS
You are browsing an online store, adding your favorite items to the cart. Before checkout, you glance at the address bar. There is a little padlock icon. Feels reassuring, right?
That tiny symbol is powered by SSL/TLS — and it’s still the unsung hero of modern web security.
But wait… isn’t SSL outdated?
Let’s unpack this. Together.
Introduction to SSL and Its Modern Relevance
It’s 2026. We’ve got AI-generated malware, ultra-targeted phishing attacks, and quantum computing knocking at the door. So why are we still talking about something invented in the 90s?
Because SSL (and now TLS) is essential.
a. What is SSL and Why Does It Still Matter?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. Think of it as a protective tunnel between your browser and the website you’re visiting.
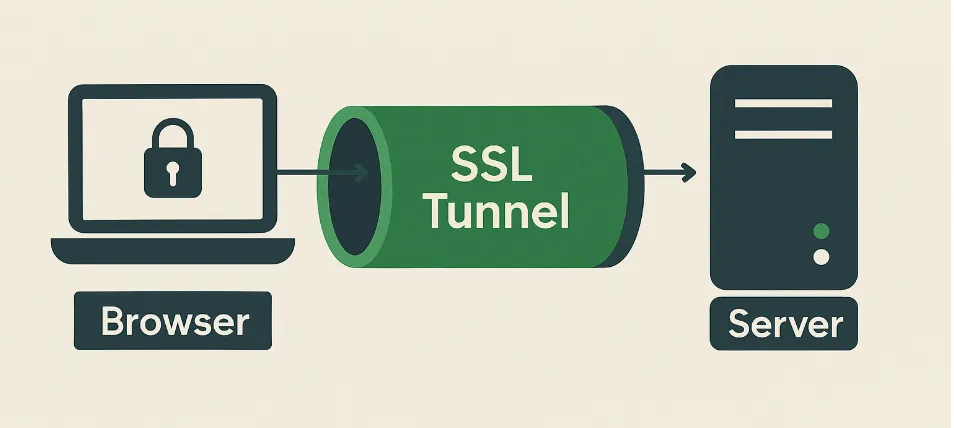
Without SSL, your data, your passwords, your credit cards, your personal info travel the internet like an open postcard.
Even though SSL is an outdated protocol, people still use the term to describe TLS, which is the modern and more secure version.
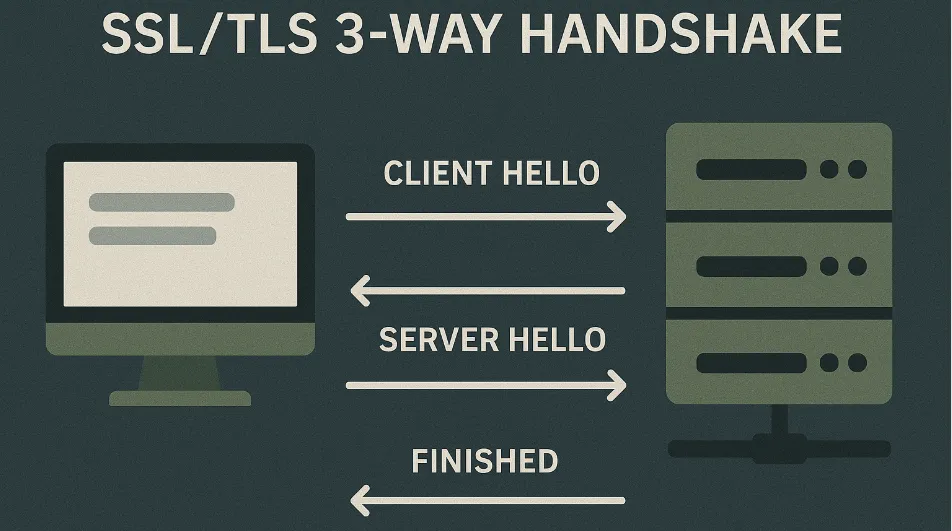
Why does it still matter? Because every time you visit a website, there’s a digital handshake happening behind the scenes.
No SSL/TLS = no trust = no visitors.
SEO Tip: Google loves HTTPS.
Since 2014, HTTPS has been a ranking signal. If you’re still running an HTTP-only website in 2025, you’re probably invisible on page 1.
So yes, SSL matters for security, trust, and search rankings.
b. The Transition: From SSL to TLS — What Changed and Why?
Let me first clear the confusion.
SSL 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0 were full of bugs and vulnerabilities. Then came TLS (Transport Layer Security), which fixed those flaws and kept evolving.
TLS is what we all use today – TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 are the current secure standards.
| Feature | SSL | TLS |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Secure Sockets Layer | Transport Layer Security |
| Release Year | 1995 | 1999 |
| Security | Less secure (deprecated) | More secure (actively maintained) |
| Handshake Process | Includes a few known vulnerabilities | Improved and more efficient handshake |
| Support | Not supported in modern browsers | Widely supported |
| Performance | Slower due to older cryptography | Faster with modern algorithms |
So even though we casually say “SSL certificate,” what we actually use is TLS.
Pro Tip: Always disable older versions like SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0/1.1. Google Chrome and major browsers already block them.
c. Why is SSL/TLS still the Cornerstone of Web Security in 2026?
It’s easy to think modern threats need modern tools. But sometimes, foundational tech like TLS does all the heavy lifting.
Here’s why it’s still important:
- It encrypts everything that is being sent between client and servers, login forms, payment data, chats.
- It prevents MITM (Man-in-the-Middle) attacks.
- It builds user trust instantly.
But wait, what is MITM attack?
Imagine you’re sending a secret message to a friend across a busy room. A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack is like someone secretly jumping between you and your friend, grabbing your message, reading it, maybe even changing it, and then sending it along.
Your friend gets the message, thinks it’s from you, and has no idea someone else intercepted it. Meanwhile, the attacker has all your private info! It’s sneaky eavesdropping, but with the power to manipulate the conversation.
Without TLS, attackers could intercept your traffic and inject malware or steal personal information. Even your SEO rankings could take a hit.
In a world filled with cyber threats, TLS is your first line of defense and your cheapest one too.

d. SSL/TLS Best Practices in 2026
Let’s talk about strategy. If you want your site to be safe, fast, and SEO-friendly then follow these practices:
1. Use TLS 1.3
This is the most secure and fastest version. It shortens the handshake, uses strong ciphers, and blocks downgrade attacks.
2. Get an SSL Cert from a Trusted CA
Use trusted Certificate Authorities like Let’s Encrypt, DigiCert, or Sectigo. Avoid shady ones.
3. Automate Certificate Renewal
Expired certs kill trust instantly. Use cron jobs, Certbot, or auto-renew tools from your hosting provider.
Did You Know?
- 95% of all websites on Google’s first page use HTTPS.
- Sites without SSL face browser warnings, high bounce rates, and zero credibility.
4. Eliminate Mixed Content
All your resources (images, JS, CSS) should load over HTTPS. Mixed content leads to browser warnings and poor SEO.
5. Implement HSTS
HTTP Strict Transport Security forces browsers to only load your site over HTTPS. It’s a smart move.
What is HSTS?
HSTS is like a smart bodyguard who, after you visit once, always forces your browser to use the secure VIP door. Even if you try the old, unsafe way, the bodyguard redirects you instantly, protecting you from sneaky attacks.
SSL Certificates: Types, Uses and Automation
Imagine landing on a website and your browser throws a big red warning:
Imagine landing on a website and your browser throws a big red warning:
“This site is not secure.”
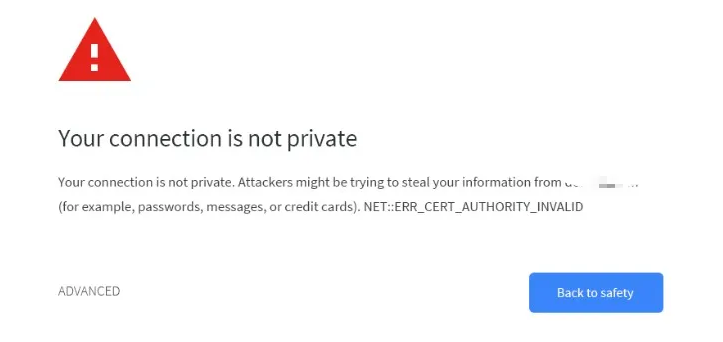
You hesitate. You bounce. And just like that, another visitor is gone.
That’s the power of SSL certificates in 2026.
And if you run a website, whether it’s a blog, store, or SaaS, you need to understand SSL like the back of your hand.
This isn’t just about that little padlock icon anymore. It’s about trust, rankings, and protecting your users.
a. Common SSL Certificate Types Explained (DV, OV, EV, Wildcard, Multi-domain)
Think all SSL certificates are the same? Think again.
They all encrypt, yes. But what sets them apart is how much they verify and what they cover.

1. Domain Validation (DV)
These are the most basic. You prove ownership of a domain, and boom you’re issued a certificate.
They’re perfect for blogs, personal sites, and non-sensitive content.
And yes, Let’s Encrypt and ZeroSSL offer these for free.
2. Organization Validation (OV)
With OV, the Certificate Authority (CA) checks your domain and your business.
These are best for small businesses, NGOs, or service sites collecting form data.
Users see more trust cues, like your verified business name.
3. Extended Validation (EV)
EV certificates go the extra mile. The Certificate Authority (CA) does a deep background check on your organization.
These are used by banks, fintech platforms, and big brands. You’ll usually see the company name in the browser address bar (depending on the browser).
Are they still useful in 2026? Some debate it but yes, if your business handles high-value transactions.
4. Wildcard SSL Certificates
Have multiple subdomains like blog.example.com, shop.example.com, and support.example.com?
A wildcard SSL covers all of them in one go. Just use a * in the domain field and you’re set.
5. Multi-Domain (SAN) Certificates
Running several unrelated domains under one business?
A multi-domain SSL (aka SAN certificate) can protect example.com, myexample.org, and another.net all under a single cert.
Perfect for web agencies or SaaS platforms with custom client domains.
Pause here, what is Certificate Authority (CA) ?
Imagine you want to prove your website is really your website, not a fake.
A Certificate Authority (CA) is like a highly trusted digital passport office. They verify your website’s identity, and if everything checks out, they issue a special digital “passport” (your SSL/TLS certificate).
When your browser sees this “passport,” it knows it can trust that the website is genuine and safe to communicate with. The CA is the ultimate trust enforcer in the web’s security system.
b. Choosing the Right Certificate: Free vs Paid
Let’s talk about the elephant in the room.
Is it worth paying for an SSL certificate in 2026?
You’ve probably heard of Let’s Encrypt.
It’s a free, automated, open Certificate Authority. And it changed the game.
But when should you go free? And when does it make sense to pay?
🆓 When to Go Free (Let’s Encrypt)
- Blogs
- Portfolios
- Dev/staging environments
- Internal apps
- Startups on a budget
Let’s Encrypt works great, is trusted by all major browsers, and renews automatically.
💳 When to Go Paid (Commercial CA)
- Enterprise sites
- Financial apps
- E-commerce stores
- Clients who need EV or OV
Paid certs come with things like warranty, better support, and manual validation.
If reputation or compliance matters, consider going commercial.
If your business handles legal, financial, or medical data, go with an OV or EV from a commercial CA.
For everything else? Let’s Encrypt is gold.
c. ACME Protocol & SSL Automation Tools
Here’s where things get nerdy (but stay with me).
Most free SSL certificates today are issued using the ACME protocol. Think of it as the behind-the-scenes robot that verifies your domain and fetches a cert.
ACME stands for Automatic Certificate Management Environment.
Do you know what is ACME?
ACME is like a clever robot that automatically gets, renews, and installs your website’s security “passports” (SSL/TLS certificates). It handles all the tricky parts, keeping your site secure on autopilot!
Let’s Encrypt started it. Now others like Buypass and ZeroSSL support it too.
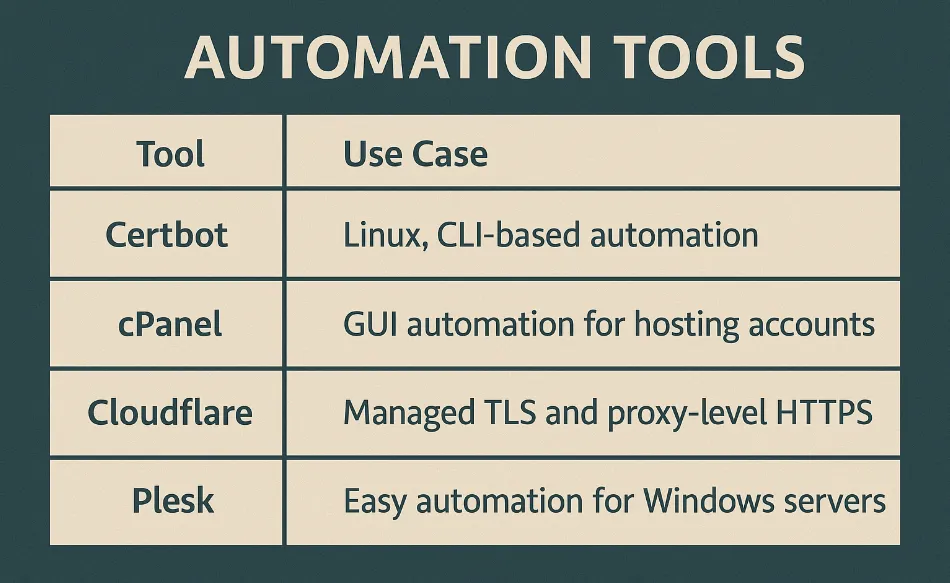
You can automate SSL issuance and renewal using:
- Certbot – The most popular tool to get Let’s Encrypt certs
- acme.sh – Lightweight and versatile shell script
- Cloudflare – Automatic HTTPS without installing a certificate at all
- cPanel & Plesk – Web hosts now offer one-click SSL via ACME
Why Certificate Automation Matters
Manual SSL renewal is a nightmare. We’ve all been there.
Your certificate expires. Your site goes down. Users vanish. Google frowns.
In 2025, automation isn’t just a “nice to have.” It’s a must.
Tip: Always automate renewal using ACME or your hosting control panel. Set it and forget it.
Bonus Tip: Use ZeroSSL or Buypass as Let’s Encrypt Alternatives
If Let’s Encrypt is down or rate-limited, tools like ZeroSSL or BuyPass offer similar features with ACME support.
d. Best Practices for Certificate Management in 2025
SSL isn’t “set and forget.” Even if it auto-renews, some hygiene is essential.
Follow these rules:
Best Practices Checklist
- Use TLS 1.3 only — Disable older versions
- Renew before expiry — Even auto-renew can fail
- Monitor expiry with tools like SSLMate or Cronitor
- Redirect HTTP to HTTPS with 301s
- Use HSTS for strict security
- Avoid mixed content — No HTTP assets on HTTPS pages
e. Certificate Transparency Logs: A Hidden Power Tool
Here’s a powerful trick not everyone uses.
Every time an SSL certificate is issued, it’s logged in a public system called Certificate Transparency (CT).
They’re public logs of all SSL certificates issued by CAs. Introduced by Google to prevent fraud.
You can use CT logs to:
- Check if someone’s spoofed your domain
- Track expiring or duplicated certs
- Monitor wildcard issuance across your org
Tools like crt.sh, Censys.io, and Google’s CT logs help you watch your certificate footprint.
Tip: Subscribe to alerts for your domain on crt.sh. It’s free and fast.